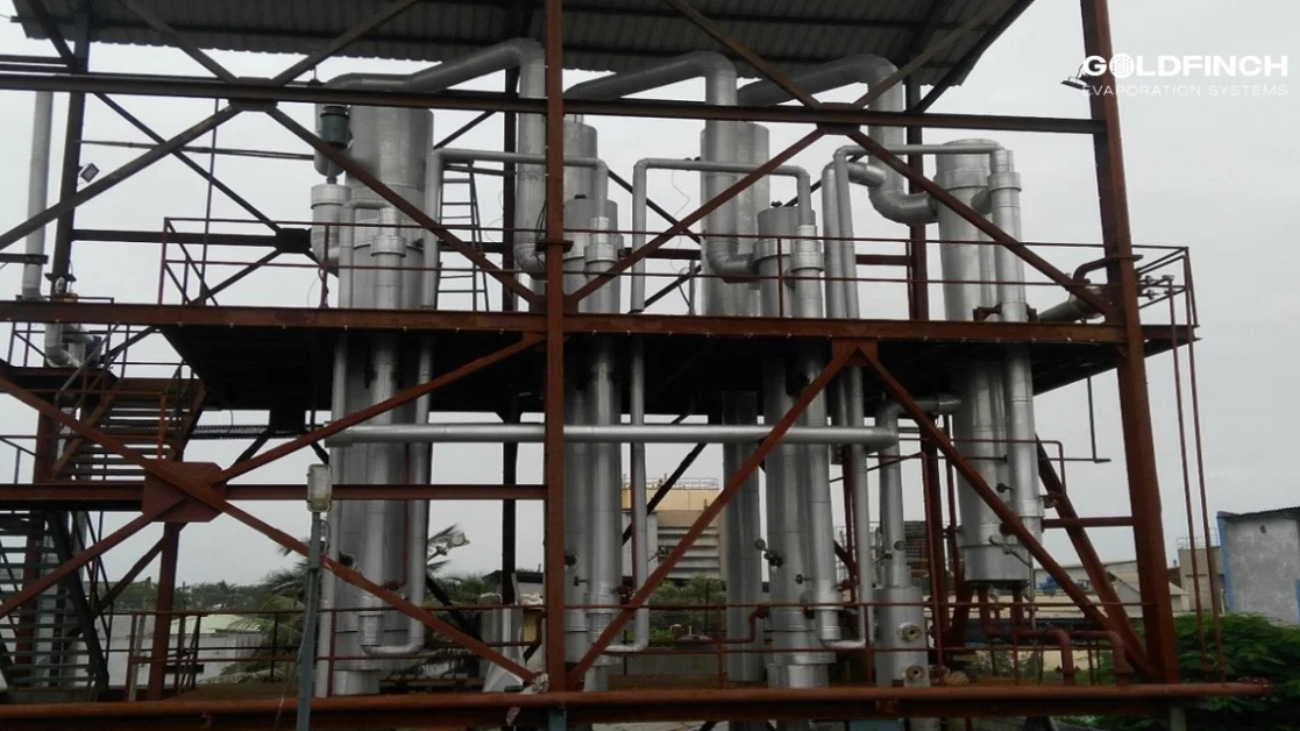
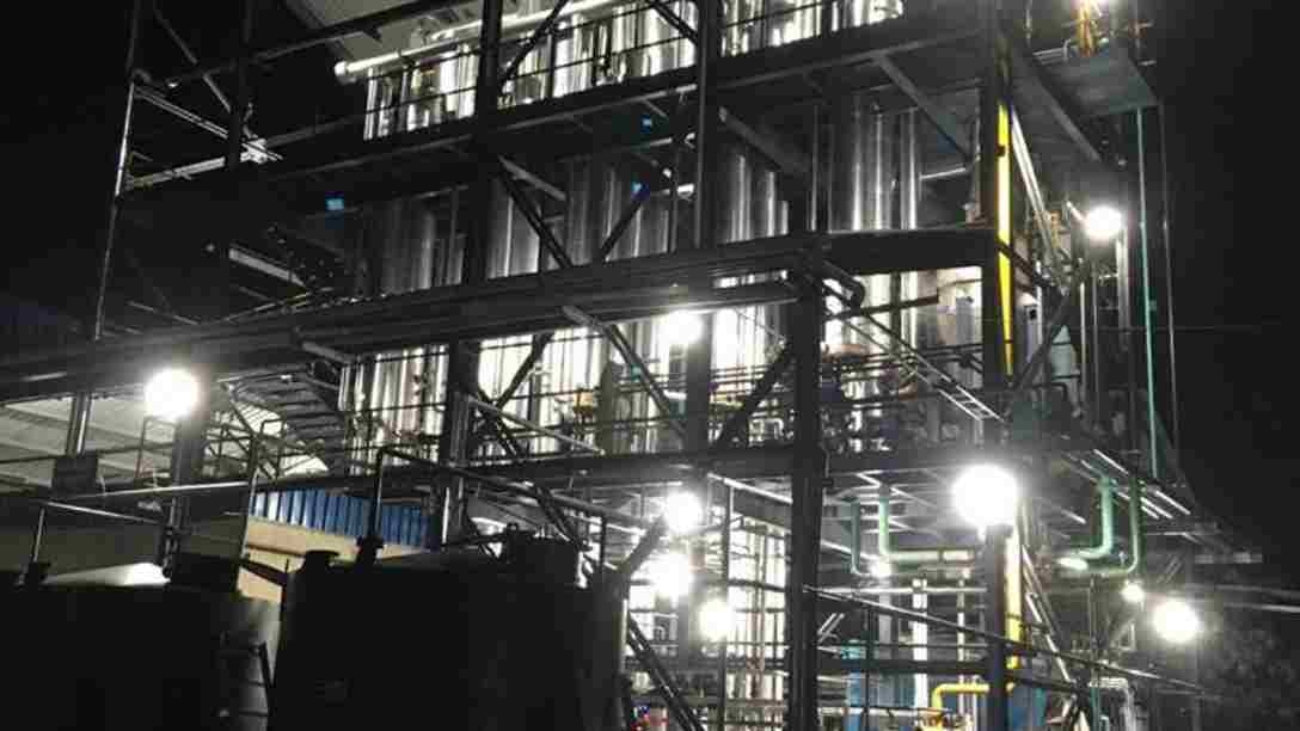
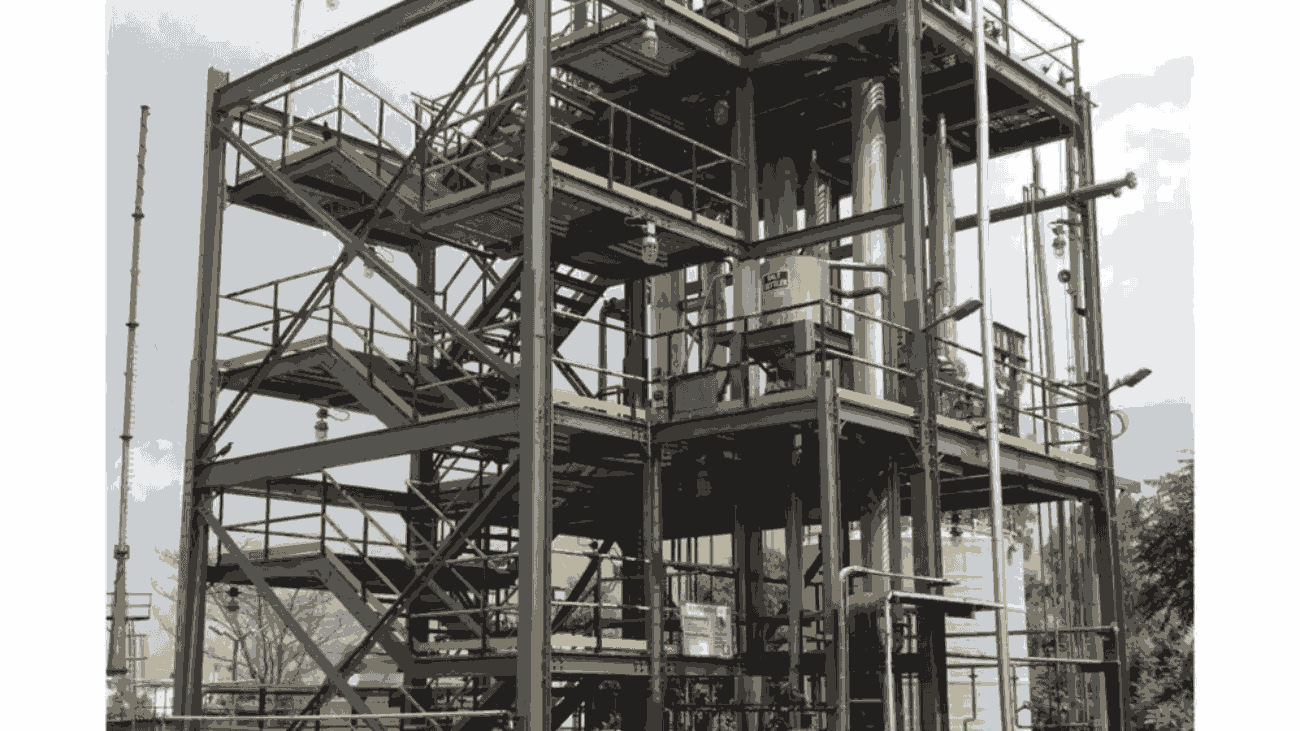
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) is an advanced wastewater treatment system that ensures no liquid waste leaves the industrial premises.
Top ZLD Plant Manufacturers in India for Effective Wastewater Treatment
Introduction: What is Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD), and why is it important?
ZLD Plant is a process by which all the wastewater created in an industrial setting is collected, treated, and recovered for reuse. The solid waste separated by this process is either disposed of or repurposed. This ensures no liquid waste leaves the industrial premises, thus making it a closed-loop system.
A Zero Liquid Discharge system has become necessary for industries set up in places of water scarcity and limited access to safe water. The rapid industrialization of some areas in India has created pressure on the natural resources in those regions. The need for conservation and sustainable use of water arises due to the lack of safe-to-use water for the people. This has made large-scale businesses rethink their water usage and take up initiatives toward responsible water treatment and disposal.
The growing need for ZLD Plant & Wastewater Treatment in Indian industries
Industries are one of the key focus areas for water conservation projects due to the significant amount of water pollution and depletion caused by them. Water-intensive industries such as thermal power plants, paper manufacturing, textiles, chemicals, iron and steel, etc, generate huge levels of wastewater contaminated with harmful chemicals and heavy metals.
This makes it very unsafe to be released back into the environment as it would end up polluting water bodies and soil. To avoid this, proper treatment of such wastewater is essential. Zero Liquid Discharge plants are required for this purpose so that industries can:
- Reuse the treated water and reduce their dependency on freshwater sources
- Comply with rules and regulations
- Help the cause of environmental conservation
- Reach the Sustainable Development Goals
Goldfinch Evaporators is one of the best ZLD plant manufacturers in the market as it has completed more than 50 projects of varying complexities for many different industries requiring pre-treatment, dissolved solids concentration, and thermal treatment.
Key industries that can implement ZLD Plant technology for Wastewater Treatment in India
There are quite a few industries in India that can benefit from adopting the Zero Liquid Discharge Plant for effective wastewater treatment, such as:
- Thermal Power Plants: The basic functioning of thermal power generation systems requires heavy water usage for running the steam turbines and cooling towers. In such cases, the industry can install ZLD technology to reuse the recovered water and reduce its usage of fresh water.
- Textile Industry: Fabric dyeing is the most water-intensive process in the making of textiles, and the used water can be put through a ZLD plant to obtain clean and reusable freshwater for the industry.
- Iron & Steel: The iron and steel factories can implement ZLD systems in their factories for better water reuse and greater efficiency.
- Paper Industry: Paper mills make use of large volumes of water in the pulping and paper-making process. The remaining sludge cannot be let back into the environment. This requires intricate ZLD processes to purify and recollect the water.
- Chemical & Pharma Industries: The manufacturing of chemicals and pharmaceutical products end up with huge amounts of chemicals in the water used. As the chemicals mixed in the water can be complex and hard to break down and separate, a large-scale and much advanced version of the Zero Liquid Discharge System is used for dealing with such type of wastewater.
Zero Liquid Discharge can be used in all such fields to ensure safe disposal and proper treatment of wastewater used for industrial purposes. Goldfinch Evaporators, the top manufacturer of Zero Liquid Discharge Systems, can design and install effective wastewater management systems in all such industries.
The Benefits of Adopting ZLD Plant Systems for Businesses and the Environment
Adopting Zero Liquid Discharge systems in any industry is a costly affair, but it is a strategic investment that pays off its costs in the long run while also reducing the environmental impact of the manufacturing process by effective wastewater treatment.
The benefits for businesses are:
- Cost savings due to reuse of water & other products
- Regulatory compliance with environmental laws
- Achieving Sustainable Development Goals
- Lower waste volumes reduce the cost of waste management
- Some processes recover vital and valuable resources
- In-house water treatment reduces the cost of transporting wastewater to a treatment facility
The benefits for the environment are:
- Reduced water & soil pollution
- Retention of water bodies & groundwater
- Better environment for the surrounding population
Businesses joining hands with Goldfinch Evaporators will greatly benefit from our ZLD plant systems, as we can help industries meet their water reuse and wastewater treatment needs.
Challenges Faced by Industries Implementing ZLD
As interesting and important as Zero Liquid Discharge Systems sound, they also come with their fair share of hurdles and challenges for industries. Some major ones are listed below:
- Costly to set up and run
- Lack of government support & funding
- Lack of awareness
- Lack of importance to environmental conservation by small & medium-scale industries
- Long period to reach break-even
- Involves complex processes to run
- Can require high energy consumption
- Handling of solid waste
- Requires hiring trained operators
Such challenges hamper the adoption of Zero Liquid Discharge systems in India’s industrial sectors.
Growing Adoption of Zero Liquid Discharge Systems in India
The Government has recognized the need and importance of ZLD Plant Systems and water recycling. This has made the installation of such water treatment plants in high-pollution industries crucial. The government is pushing for the adoption of ZLD via financial support and regulation compliance.
These compliances are monitored by the Pollution Control Boards. In certain areas of water scarcity, the government has understated the use of ZLD plants for industries. All such measures just make it more sensible for industries to get together with Goldfinch Evaporators, the best manufacturer of ZLD systems in India, to fulfill their water recycling goals.
Conclusion: Embracing Zero Liquid Discharge to Secure India’s Environmental Future
With the rate at which industries are growing in our country, it is important to make sure that we are doing so in a sustainable way. Rapid industrialization can lead to environmental concerns getting overlooked by businesses and causing long-term, irreversible harm to our precious natural resources and surroundings. The implementation of Zero Liquid Discharge Systems enables water recycling, better disposal of solid waste, reusing of the byproducts, and also saves the surroundings from pollution.
Goldfinch Evaporators enables businesses to get sustainable and efficient wastewater & water treatment solutions cost-effectively!
Feel free to follow us on LinkedIn.
Zero Discharge System: Comprehensive Wastewater Treatment Explained
Goldfinch leads Zero Discharge Systems in India, offering advanced solutions for wastewater treatment and resource recovery.
What is Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) and why does it matter?
One thing Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) stands for is the treatment of water waste. This is so that no liquid waste gets discharged into the environment. It recycles and reuses water, thus contributing positively to environmental sustainability and reducing water pollution. Its mention is important, especially in industries using water intensively, coupled with strict environmental regulations.
Zero Liquid Discharge is Important
ZLD systems are vital for water conservation and protecting the environment. Here are some reasons made by ZLD as essential:
Environmental Protection:
Zero Liquid discharge elimination prevents water pollution.
Prevents harmful contaminants from going into the water bodies.
Water conservation:
Recycle up to 95% of wastewater.
Save freshwater resources.
Compliances with the regulation:
There are strict environmental laws and regulations set to comply.
Avoids penalties that benefit corporate images.
Cost Effectiveness:
Procurement costs of water are resulting in reductions.
Reduced waste disposal cost.
Advantages of Application of Zero Liquid Discharge Systems
Some of these advantages include:
Optimal Utilization of Resources: Maximize all water recovery and reuse.
Better Operational Sustainability: Less environmental impact.
Enhanced Corporate Responsibility:
Show their commitment to sustainability.
Zero Liquid Discharge System Risk
While a maximum or near complete ZLD system has tremendous benefits, it also comes with some drawbacks:
Heavy Capital Outlay: Setup and installation are expensive.
Energy-Intensive Processes: Require a lot of energy to work.
Complex Maintenance: Requires the specialized skill of maintaining.
What is a ZLD System?
A Zero Liquid Discharge System (ZLD) is a specific aspect of water treatment, wherein water is made available from all sources, and all forms of waste are transformed for recovery and reuse. It generally includes the following processes:
Pretreatment: All suspended solids and solids are separated from the fluids.
Evaporation: Concentration of waste using evaporators.
Crystallization: Converts waste to rid it in solid form.
Below are the distinctions between Minimum Liquid Discharge and Zero Liquid Discharge:
Minimum Liquid Discharge (MLD):
It is designed to discharge liquids to the least minimum level possible; less severe than ZLD, but still promotes water conservation.
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD):
It will not permit any discharge of liquid.
Makes 100% recovered water.
Zero Liquid Discharge in India
India faces acute water scarcity and stringent environmental norms, making ZLD systems a critical solution for industries. The government actively promotes ZLD adoption in:
Textile Industry
Power Plants
Chemical Manufacturing
Pharmaceutical Sector
Explore Goldfinch ZLD Evaporators
Goldfinch Evaporators has been a leading manufacturer of ZLD systems in India for over four decades. Our innovative vapor recompression solutions cater to diverse industrial applications, ensuring high efficiency and sustainability.
Why Choose Goldfinch ZLD Evaporators?
Compact Design:
Space-efficient systems.
Easy integration with existing setups.
High Efficiency:
Advanced technology for maximum water recovery.
Energy-efficient processes.
Customizable Solutions:
Tailored to specific industry requirements.
Scalable systems for diverse needs.
Related Resources
Zero Liquid Discharge Systems Overview
- A comprehensive guide on ZLD technology
- Detailed insights into system components and processes.
Benefits of ZLD Implementation
- Case studies from various industries.
- Statistical analysis of water savings and cost efficiency.
Challenges in ZLD Adoption
- Exploring common barriers and solutions.
- Strategies to overcome technical and financial constraints.
Conclusion
Zero Liquid Discharge is not just a regulatory necessity but a critical step toward sustainable industrial operations. Industries that implement ZLD systems can save water, decrease environmental impact, and comply with strict standards. Goldfinch Evaporators, with its innovative solutions and decades of expertise, is your trusted partner in achieving zero liquid discharge goals.
Below are some related links – https://goldfinchevaporators.com/zero-liquid-discharge-zld-india/
Understanding Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD)
What does Zero Liquid Discharge mean?
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) is an advanced system designed to prevent any liquid waste from leaving an industrial facility. Instead, the purified effluent and solid waste disposal form the
the core of such an environmentally-friendly operation towards sustainable industrialization thereby minimizing waste discharge and putting less strain on the natural water resources.
Explanation of ZLD and its Necessity
Essentially, ZLD comprises a collection of processes that make usable water from the effluents of industries. The remaining solids are either reused or safely discarded. This system is more important in water-scarce areas because it involves the conservation of water and reduction in pollution of the environment.
ZLD Systems – Their Purpose
Protecting the environment: It eliminates all the hazardous and polluting liquid waste, thereby destroying water bodies as well as damaging ecosystems.
Water recycling: It is an efficient method through which industries can recycle and reuse water, thereby reducing the amount of freshwater they consume.
Regulatory Compliance: The ZLD has become increasingly necessary to meet very high environmental laws and regulations.
Cost-effective: Although the cost involved is pretty high initially, in the long run, ZLD systems prove cost-effective by recycling water and decreasing waste disposal expenditure.
ZLD Treatment
Usually, the following stages signify the ZLD process:
Pretreatment: Removal of all the largest applications and any contaminants within the wastewater.
Evaporation: Concentration of the waste stream using methods like Multi-Effect Evaporation (MEE) or Mechanical Vapor Recompression (MVR).
Crystallization: Primary salts and some other residuals become solidified for disposal or reuse.
Condensation: Purified water is put back into use in the industrial system.
Classification of ZLD Evaporators
Goldfinch Evaporators is specialized in ZLD systems, a few of which include:
Multiple Effect Evaporators (MEE): Makes use of multiple stages to increase energy efficiency.
Mechanical Vapor Recompression Evaporators (MVR): Recycle the vapor through compression for maximization of energy savings.
Thermal Vapor Recompression Evaporators (TVR): It is a combination of mechanical and thermal processes for maximum efficiency.
How Does a ZLD Treatment System Work?
Characteristically, ZLD Treatment Systems treat waste streams by these methods: Filtration, Evaporation, and Crystallization. The process recycles purified water separately from solid waste and achieves zero liquid waste discharge for sustainable industrial operations.
Primary Components of Basic ZLD Treatment System
Filtration Units: Primary treatment of wastewater.
Evaporators: Concentration of waste streams.
Crystallizers: Dissolved substances are converted into solids.
Condensers: Recoverance of clean water for reuse.
Application of Zero Liquid Discharge in Industries
ZLD is primarily applicable to industries like power generation, chemicals, textiles, and others. Such industries, having a high volume of wastewater, recover resources and act on the global sustainability agenda.
ZLD Regulations and Guidelines in India
Zero liquid discharge is a compulsory mandate in many water-scarce regions, particularly for highly polluted effluents. Hence, the state has put in place provisions to enforce strict compliance by all facilities to encourage sustainability in these industries.
Advantages of Goldfinch ZLD Evaporators
Goldfinch Evaporators is one of the most reputed manufacturers of ZLD systems in India and offers:
Compact Designs: Space-efficient industrial solutions tailored to the industry’s needs.
Innovative Technology: Cutting-edge vapor recompression technology.
Experience: Over 40 years of involvement in the manufacture of evaporators.
Custom Solutions: Systems designed to meet the specific requirements of the industry.
Why Choose Goldfinch Evaporators?
Goldfinch Evaporators specializes in sustainable solutions for the management of industrial wastewater. The said ZLD systems are designed and ensured to perform well-permitting compliance with the environmental standards as well as improved efficiency in usage.
Conclusion
Zero Liquid Discharge is a significant step toward more sustainable water management in enterprises. Through the implementation of ZLD systems, companies could help less impact on the environment, maintain regulations, and better use of resources. Goldfinch Evaporators happens to be ahead in the industry when it comes to innovation and efficiency, making them the smart choice for ZLD systems in India and beyond. Adopt ZLD today for a better tomorrow and a sustainable future.
To Know More Visit This Link – https://goldfinchevaporators.com/zero-liquid-discharge-zld/
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD): An Every Industry Guide
Introduction
One cutting-edge treatment method that guarantees zero waste release into the environment is Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD). ZLD supports industrial sectors in maintaining sustainability and adherence to environmental requirements, particularly in India. This manual examines the ZLD system, its advantages, its uses in different sectors, and how Goldfinch Evaporators contribute to the supply of superior ZLD solutions.
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD): What Is It?
Definition and Goals of ZLD
One treatment technique that guarantees full wastewater recycling is zero liquid discharge. This technology reduces pollution by allowing industries to recover and reuse all of the water while safely removing solid waste.
The Significance of ZLD in Environmental Sustainability
Recognizing the Effects on the Environment
Untreated industrial wastewater flow can contaminate nearby waterways, endangering human health and ecosystems. ZLD solves this by making it possible for businesses to recycle and cut waste.
India’s Regulatory Push for ZLD
To lessen water pollution, the Indian government requires ZLD for sectors like chemicals, medicines, and textiles. ZLD also complies with environmental laws, which are getting more stringent all around the world.
Zero Liquid Discharge’s (ZLD) Advantages
Conserving Water
By enabling enterprises to recycle 95–99% of wastewater, ZLD helps them save water and lessen their reliance on outside water sources.
Diminished Effect on the Environment
ZLD lowers the risk of pollution and safeguards nearby water bodies by banning wastewater outflow.
Long-Term Cost Effectiveness
Despite the initial outlay, ZLD lowers the cost of water procurement, which eventually results in savings.
Adherence to Regulations
Businesses that use ZLD adhere to environmental standards, preventing penalties and limitations.
Important Sectors Gaining from ZLD Technology
The Textile Sector
Strict discharge requirements apply to textile producers. They can recycle water and maintain compliance by implementing ZLD.
Pharmaceutical and Chemical Industries
Large amounts of wastewater are produced by these industries. ZLD reduces pollution by facilitating safe and efficient wastewater management.
Power Generation
Power plants ZLD helps power plants save water and follow environmental regulations.
The Food and Drink Sector
In order to preserve nearby water sources, ZLD makes sure that these establishments are able to handle their wastewater, which frequently contains organic waste.
What’s the Process of ZLD?
1. Wastewater pre-treatment
First, wastewater is cleaned to get rid of organic compounds, oils, and big particles.
2. Effluent Concentration
Wastewater is concentrated using technologies such as Mechanical Vapor Recompression (MVR) and Multi-Effect Evaporators (MEE).
3. The Process of Crystallization
The concentrated waste separates from the water by a process called crystallization, in which solid waste forms.
4. Recovery and Reuse of Water
While solid trash is disposed of safely or put to other uses, recovered water is filtered and employed again in the industry.
ZLD and MVR Technology Distinctions
MVR, or mechanical vapor compression
MVR, a crucial technology in the ZLD process, uses less energy by compressing vapor to concentrate effluents. It is perfect for businesses trying to maximize water treatment energy efficiency.
MVR Vs. ZLD
MVR is an effective instrument inside ZLD, which is a holistic solution centered on zero discharge. MVR is an essential part of sustainable ZLD systems because it concentrates on lowering evaporation energy consumption.
ZLD in India: Policies and Procedures
ZLD in India requirements for industries are strict. In order to control wastewater outflow, ZLD must be implemented, especially in the chemical and textile industries. In order to safeguard water resources and encourage sustainable behaviors, the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) enforces these rules.
Goldfinch Evaporators’ Function in ZLD Solutions
Based in Thane, Mumbai, Goldfinch Evaporators is a top supplier of ZLD, MVR, and evaporators. Their technologies are made to help businesses minimize their impact on the environment by achieving zero discharge with maximum efficiency.
Ideas for Subheadings:
The Significance of ZLD in Environmental Preservation
Sectors Using ZLD Systems
A Comprehensive Understanding of the ZLD Process
Zero Liquid Discharge Benefits
Implementing ZLD Technology Presents Difficulties
Leaders in ZLD Solutions: Goldfinch Evaporators
Conclusion
A revolutionary method for managing industrial wastewater is Zero Liquid Discharge. ZLD helps enterprises meet regulations, save water, and lessen their environmental effect. Leading the way in this technology is Goldfinch Evaporators, which provides efficient ZLD and evaporator solutions that help businesses and advance environmental objectives.
To Know More Visit this Blog
What is Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) in the Fertilizer Industry?
Optimizing Efficiency: Your Complete Guide to Picking the Best Multi-Effect Evaporator Manufacturer
Multi-Effect Evaporator Manufacturer
In most industries to improve processes and cut down costs, the selection of the right Multi-Effect Evaporator manufacturer plays a crucial role. Be it in food, chemical, or wastewater engineering, industrial evaporators will have a major effect on the overall performance, the amount of energy consumed, and the environmental impact. This blog will help you pick the most appropriate manufacturer while looking at Mechanical Vapour Recompression Evaporators (MVRE) systems, and Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) systems.
Grasping the Concept of Multi-Effect Evaporators
When it comes to the process of concentrating liquids by the removal of water, multi-effect evaporators(MEE) are utilized in plenty of industrial processes today. The process utilizes several stages (effects) all making use of vapour produced from the last stage which vaporization consumes less energy. Such systems are crucial to sectors that generate a lot of effluent and that aim at reducing the quantity of water released to the environment.
Key Features of Multi-Effect Evaporators:
- Highly energy-efficient
- Reduced operational costs
- Minimal water wastage
- Easy to maintain
The Concept of Mechanical Vapour Recompression Evaporators (MVRE): A Revolution
Ever since the invention of mechanical evaporator units (MEU), those mechanical vapor recompression evaporators (MVRE) turn the efficiency knob on a notch higher. In mechanical vapor recompression evaporators, the evaporated liquid’s vapor is compressed to enhance its temperature and this is subsequently utilized in the evaporation cycle. This leads to extreme reduction in energy consumption hence considered a green solution as well as an economical one.
Benefits of MVRE:
- Up to 90% energy savings
- Lower carbon footprint
- Extended equipment life due to reduced mechanical wear
- Reduced dependence on external energy sources
Environmental Views on Waste Management: Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD)
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) systems do not allow liquid wastewater to leak into external equipment.. For water-intensive sectors looking to recycle water and cut down on wastewater production, such systems are crucial. In sectors where environmental compliance is highly valued, like textile, power generation, and medicine, such solutions are perfect.
Why Choose ZLD?
- Eliminates wastewater discharge
- Recycles water for reuse
- Reduces environmental impact
- Complies with environmental regulations
Criteria for Choosing the Best Manufacturer for Multi-Effect Evaporators
One of the challenges faced by the buyer is the Multi-Effect of manufacturers that produce MEE, MVRE, ZLD, etc. Therefore, it is important to select an appropriate one that will fulfill your specific requirements. The following are some of the considerations that ought to be made when choosing a manufacturer:
Experience and Expertise:
Ensure that the potential suppliers you tap produce high-quality evaporators. Most likely, companies that have spent a lot of years producing evaporators such as Goldfinch Evaporators tend to have more grasp on the issues within the industry and the problems that the client needs solved.
Customization Options:
Your operations may have specialized equipment that will be within the configuration of your plant. Manufactures who also provide custom made evaporators for special purposes will be more suitable to your needs.
Energy-efficiency:
In today’s inexpensive and green world, energy conscious designs are paramount. Minimizing your long term running costs will also be aided by manufacturers who utilize advanced in energy saving technologies such as MVRE and multi-effect designs.
Sustainability Solutions:
A visionary manufacturer in this day and age will also provide solutions that are not contrary to sustainability. For instance, Goldfinch Evaporators enables companies to practice regulatory compliance without adverse environmental impacts by utilizing ZLD technologies.
After-Sales Support and Maintenance:
The best manufacturers provide complete after sales support, which guarantees that the evaporators will be functional for a long time. It is critical to provide these services: routine maintenance and repair, troubleshooting, and replacement of broken parts
Working with Goldfinch Evaporators:
Advantages
In terms of designing and producing Mechanical Vapour Recompression Evaporators, Multiple Effect Evaporators, and Zero Liquid Discharge systems, Goldfinch Evaporators is a pioneer. For several reasons, you ought to think about working with Goldfinch:
Originality: Goldfinch Evaporators provides the most recent technologies of MVRE and ZLD systems with an aim to improve the efficiency of operation in a more sustainable manner.
Adaptability: All the industries present have different challenges and Goldfinch addresses such by offering varying approaches for different purposes.
Market Knowledge: Considering the number of industries Goldfinch has operated within, it can be safely said that it ensures its evaporators are efficient and effective in optimization of performance.
Customer Care: The said company provides efficient services even after selling the evaporators, factors which enable all the evaporators to function properly for the period they are meant to work.
Concept of Multi Effect Evaporators
Mechanical Vapour Recompression Evaporators (MVRE): Technology that Changes The Game
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD): An Environmental Friendly Approach
Conclusion
To summarize, the selection of a suitable Multi-Effect Evaporator (MEE) manufacturer is critical for achieving maximum efficiency and ensuring durability. Goldfinch Evaporators, thanks to the company’s mastery of MVRE and ZLD systems, provides advanced, energy-efficient systems that cater for the needs of any industry. The right evaporator technology adoption can cause a business to incur lower operational costs, protect the environment through adherence to regulations and help run the business efficiently.
Concentrating on these primary aspects enables the business to take the right steps and reap the benefits of dependable and high-performing environmentally safe evaporation solutions. Reach out to Goldfinch Evaporators to find out how we can assist you in fine-tuning your operations.
What is Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) in the Fertilizer Industry?
In the realm of sustainable industrial practices, Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) stands out as a pivotal solution, particularly in the fertilizer industry. This comprehensive guide explores what ZLD entails, its significance in the fertilizer sector, and how companies like Goldfinch Evaporators Systems are leading the charge in implementing this advanced technology.
Understanding Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD)
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) is a water treatment process that aims to eliminate all liquid discharge from a system. In simpler terms, it ensures that no liquid effluent leaves the industrial facility or enters the environment. This approach is crucial in industries like fertilizers, where wastewater can contain harmful pollutants such as heavy metals, salts, and organic compounds.
Importance of ZLD in the Fertilizer Industry
The fertilizer industry plays a vital role in global agriculture by providing essential nutrients for crop growth. However, its operations generate significant volumes of wastewater containing concentrated salts and nutrients. Without proper treatment, this wastewater can pollute water bodies and harm ecosystems.
Benefits of Implementing ZLD in Fertilizer Plants
- Environmental Conservation: By preventing liquid discharge, ZLD helps protect water resources and ecosystems from pollution.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many regions enforce stringent regulations on wastewater discharge. ZLD ensures compliance with these standards.
- Resource Recovery: ZLD systems often include processes for recovering valuable resources from wastewater, such as salts and nutrients, which can be reused in fertilizer production.
How ZLD Works in the Fertilizer Industry
Evaporation and Crystallization Processes
Goldfinch Evaporators Systems employs advanced evaporation and crystallization technologies in their ZLD systems. These processes involve:
- Multi-effect Evaporation: Utilizing multiple stages of evaporation to concentrate wastewater and minimize water discharge.
- Crystallization: Precipitating dissolved salts from the concentrated solution, producing solid crystals that can be safely disposed of or reused.
Case Studies: Successful Implementation of ZLD
Goldfinch Evaporators Systems has successfully implemented ZLD solutions in several fertilizer plants worldwide. These case studies demonstrate:
- Reduction in Environmental Impact: Significant reduction in wastewater discharge and pollution levels.
- Operational Efficiency: Improved operational efficiency and cost savings through resource recovery and compliance with regulations.
Challenges and Solutions in ZLD Adoption
Despite its benefits, adopting ZLD in the fertilizer industry presents challenges such as high initial costs and operational complexities. However, companies like Goldfinch Evaporators Systems address these challenges through:
- Customized Solutions: Tailoring ZLD systems to specific plant requirements.
- Technological Innovations: Continual advancements in ZLD technologies to improve efficiency and reduce costs over time.
Future Outlook: Advancements in ZLD Technology
The future of ZLD in the fertilizer industry looks promising with ongoing research and development focusing on:
- Energy Efficiency: Enhancing energy recovery from wastewater treatment processes.
- Integration with Circular Economy: Developing closed-loop systems that maximize resource recovery and minimize waste generation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) is not just a technology but a sustainable solution that aligns with the fertilizer industry’s commitment to environmental stewardship and regulatory compliance. Companies like Goldfinch Evaporators Systems are at the forefront of integrating ZLD technologies, ensuring efficient and responsible management of wastewater. By understanding and embracing ZLD, fertilizer plants can achieve operational excellence while contributing to a cleaner and more sustainable future.
To Know More Visit This Link – https://goldfinchevaporators.com/30-kld-triple-effect-evaporator-for-rupa-organics-taloja/
The (Zero Liquid Discharge) ZLD in Textile Industry
Introduction
The textile industry is a cornerstone of the Indian economy, contributing significantly to the national GDP and export earnings. However, the sector’s heavy reliance on water for dyeing and coloring poses significant environmental and operational challenges. As water scarcity intensifies and environmental regulations tighten, sustainable water management has become paramount. Enter Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) technology—a transformative approach that addresses wastewater management and promotes water conservation and resource recovery. Let’s study how ZLD in the Textile Industry plays a vital role, especially in Indian textile manufacturing industries.
Also Read: Understanding Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD): Principles and Process
Understanding ZLD in Textile Industry
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) is a comprehensive wastewater treatment process that ensures no liquid waste is discharged into the environment. This method involves treating, recycling, and reusing wastewater, thereby significantly reducing the intake of fresh water and minimizing environmental pollution. ZLD desalination, in particular, can recover 75%–90% of the total water from wastewater, making it a high-recovery process ideal for the textile industry.
Components of a ZLD System
A well-designed ZLD system integrates several key components:
- Pretreatment (Physicochemical and Biological)
- Reverse Osmosis (RO) Membrane Processes
- Evaporators and Crystallizers (Thermal Processes)
Technologies Employed in ZLD
Several advanced technologies are utilized to achieve ZLD:
- Thermal Processes: Multistage Flash Distillation (MSF), Single and Multiple Effect Evaporation (SEE/MEE) coupled with Mechanical Vapor Compression (MVC).
- Membrane-Based Systems: Reverse Osmosis (RO), Forward Osmosis (FO), Membrane Distillation (MD), Nanofiltration (NF), and Electrodialysis (ED/EDR).
Also Read: Multiple Effect Evaporators Manufacturer Supplier
Driving Factors for ZLD Adoption
The adoption of ZLD in Textile Industry is driven by several factors:
- Fresh Water Scarcity: Increasing water demand and declining availability necessitate efficient water management.
- Water Economics: Rising water costs make recycling and reuse economically beneficial.
- Environmental Regulations: Stringent regulations mandate the reduction of wastewater discharge and pollution.
ZLD in the Indian Textile Industry
India, with its significant share of the global population and limited water resources, faces acute water stress. The government has implemented ZLD guidelines for key industrial sectors, including textiles, tanneries, distilleries, and pulp & paper. The 2015 ZLD mandate requires textile industries with substantial effluent discharge to achieve ZLD, with specific regulations for industries in environmentally sensitive areas.
Case Study: Tirupur Textile Cluster
The textile hub of Tirupur in Tamil Nadu has been at the forefront of ZLD implementation since 2008. The high court’s mandate for ZLD systems in dyeing and wet processing units has resulted in significant advancements in wastewater management. Here, ZLD systems have demonstrated the capability to recycle 92-95% of water and recover salts for reuse in dyeing processes.
Financial Viability and Challenges
Despite its environmental benefits, ZLD implementation poses financial challenges:
- High CAPEX and OPEX: Initial setup and operational costs are substantial.
- Management of Toxic Waste: Treatment processes generate highly toxic waste.
- Space Requirements: Large-scale ZLD systems require significant space.
- Impact on Product Cost: Increased costs can affect the final product’s pricing.
However, large-scale industries and those with high water usage can achieve ZLD through dedicated effluent treatment plants or by partnering with Common Effluent Treatment Plants (CETPs).
Technological Solutions for ZLD in Textile Industry
The textile industry deals with various types of effluents, primarily from dyeing and finishing processes. The effluent often contains high levels of salts and organic compounds, which need specialized treatment methods. Below are the primary technologies and steps used in achieving ZLD in Textile Industry:
1. Pre-Treatment Processes
- Biological Treatment: Removes biodegradable organic matter using microbial action.
- Physicochemical Treatment: Involves coagulation, flocculation, and sedimentation to remove suspended solids and reduce chemical oxygen demand (COD).
2. Membrane Technologies
- Reverse Osmosis (RO): Separates water from dissolved salts and other contaminants, achieving a recovery rate of up to 80%.
- Nanofiltration (NF): Targets specific molecules and multivalent ions, complementing RO in treating textile effluents.
- Forward Osmosis (FO) and Membrane Distillation (MD): Emerging technologies offering potential cost and energy savings.
3. Thermal Technologies
- Multi-Effect Evaporation (MEE): Utilizes multiple stages of evaporation to concentrate brine solutions.
- Mechanical Vapor Recompression (MVR): Recompresses vapor generated during evaporation to reuse energy, enhancing efficiency.
Benefits of ZLD IN Textile Industry
Implementing ZLD in Textile Industry offers numerous benefits:
- Water Conservation: Significant reduction in fresh water intake through high recovery and recycling rates.
- Resource Recovery: Recovery of salts and other chemicals reduces the need for raw materials.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meets stringent environmental regulations, avoiding potential fines and operational shutdowns.
- Sustainable Operations: Enhances the industry’s sustainability profile, attracting eco-conscious customers and investors.
Economic Implications of ZLD
While ZLD in Textile Industry systems entails high initial and operational costs, the economic benefits over time can be substantial. The cost of water saved, and recovered resources such as salts, can offset a portion of these expenses. For example, in Tirupur, the cost of recovered water ranges from Rs. 40 to 60 per kiloliter (KL), while the cost for freshwater stands at Rs. 70/KL. Additionally, the recovery of global salt, commonly used in dyeing, can further reduce operational costs.
Policy Framework and Future Prospects
India’s policy framework for ZLD in Textile Industry sets a precedent for other industrial sectors. The national mandate for textile industries emphasizes the importance of sustainable wastewater management. The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) plays a crucial role in enforcing these regulations, ensuring that industries comply with ZLD requirements.
Goldfinch Evaporation Systems: Leading the Way in ZLD Solutions
At Goldfinch Evaporation Systems, we are committed to providing cutting-edge ZLD solutions tailored to the needs of the textile industry. Our advanced technology portfolio includes high-efficiency evaporators, robust RO systems, and innovative pre-treatment solutions designed to maximize water recovery and minimize waste.
Why Choose Goldfinch Evaporation Systems?
- Proven Expertise: With years of experience in ZLD implementation, we offer reliable and effective solutions.
- Customizable Systems: Our solutions are tailored to meet the specific needs of each client, ensuring optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.
- Sustainable Practices: We focus on reducing environmental impact through innovative and efficient technologies.
Detailed Implementation Strategies for ZLD in Textile Industry
To fully understand the implementation of ZLD in Textile Industry, it’s important to delve into the detailed strategies and steps involved. This section explores the step-by-step process, technologies, and best practices that can be adopted to achieve effective ZLD.
1. Initial Assessment and Feasibility Study
Before implementing ZLD, it is crucial to conduct an initial assessment and feasibility study. This includes:
- Water Audit: Assessing the current water usage, identifying sources of wastewater, and understanding the quantity and quality of effluents.
- Feasibility Study: Analyzing the economic, technical, and environmental feasibility of implementing ZLD.
2. Pre-Treatment Processes
Effective pre-treatment is essential to prepare the wastewater for subsequent advanced treatment processes. This includes:
- Screening: Removing large solids and debris from the wastewater.
- Chemical Precipitation: Adding chemicals to remove suspended solids and reduce chemical oxygen demand (COD).
- Biological Treatment: Using microbial action to degrade organic pollutants.
3. Advanced Treatment Processes
After pre-treatment, advanced treatment processes are employed to achieve high levels of water recovery. These include:
- Membrane Technologies:
- Reverse Osmosis (RO): Using semi-permeable membranes to remove dissolved salts and contaminants.
- Nanofiltration (NF): Targeting specific molecules and ions, complementing the RO process.
- Thermal Technologies:
- Multi-Effect Evaporation (MEE): Using multiple stages of evaporation to concentrate brine solutions.
- Mechanical Vapor Recompression (MVR): Enhancing energy efficiency by recompressing vapor generated during evaporation.
4. Resource Recovery
One of the key benefits of ZLD is the recovery of valuable resources from wastewater. This includes:
- Water Recovery: Recycling up to 95% of water for reuse in industrial processes.
- Salt Recovery: Recovering salts used in the dyeing process, such as glober salt, which can be reused.
5. Waste Management
Managing the waste generated during the ZLD process is crucial to minimize environmental impact. This includes:
- Handling Toxic Sludge: Safely disposing or treating highly toxic sludge generated during the treatment process.
- Brine Management: Managing concentrated brine solutions to prevent environmental contamination.
6. Monitoring and Optimization
Continuous monitoring and optimization of the ZLD system are essential to ensure its efficiency and effectiveness. ZLD in Textile Industry includes:
- Regular Monitoring: Tracking the performance of the ZLD system, including water recovery rates and quality of treated water.
- Optimization: Implementing process improvements and adopting new technologies to enhance system efficiency.
Challenges and Solutions in ZLD Implementation
Implementing ZLD in Textile Industry comes with its set of challenges. However, with strategic planning and innovative solutions, these challenges can be effectively addressed.
1. High Capital and Operational Costs
Challenge: The initial investment and operational costs for ZLD systems are high. Solution: Partnering with specialized providers like Goldfinch Evaporation Systems can help optimize costs through customized solutions and efficient technologies.
2. Space Requirements
Challenge: ZLD systems require significant space for installation. Solution: Modular and compact system designs can be employed to fit within existing industrial spaces without extensive modifications.
3. Toxic Waste Management
Challenge: The treatment process generates highly toxic waste. Solution: Implementing advanced waste management techniques and partnering with certified waste disposal services ensures safe handling and disposal.
4. Impact on Product Cost
Challenge: Increased costs can affect the final product’s pricing. Solution: Efficient resource recovery and process optimization can offset some of the costs, making ZLD economically viable in the long run.
Best Practices for ZLD Implementation
To ensure successful implementation ZLD in the textile industry, the following best practices should be adopted:
- Stakeholder Engagement: Involving all stakeholders, including management, employees, and regulatory bodies, ensures smooth implementation and compliance.
- Skilled Workforce: Training and developing a skilled workforce to operate and maintain ZLD systems.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly reviewing and updating processes to incorporate new technologies and improve system efficiency.
- Regulatory Compliance: Staying updated with regulatory requirements and ensuring compliance to avoid penalties and operational disruptions.
Future Trends in ZLD IN Textile Industry
The future of ZLD in Textile Industry is promising, with ongoing research and development driving advancements in technology and efficiency. Key trends to watch include:
- Emerging Technologies: Adoption of newer technologies such as Forward Osmosis (FO) and Membrane Distillation (MD) that offer potential cost and energy savings.
- Digitalization: Integration of digital tools and IoT for real-time monitoring and optimization of ZLD systems.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Increasing focus on sustainability will drive the adoption of ZLD as a standard practice in the textile industry.
Conclusion
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) is revolutionizing wastewater management in the textile industry, offering a sustainable and effective solution to water scarcity and pollution. Despite the challenges associated with its implementation, the long-term benefits of ZLD in terms of water conservation, resource recovery, and regulatory compliance make it an indispensable strategy for the industry.
Goldfinch Evaporation Systems is leading the way in providing comprehensive ZLD solutions tailored to the specific needs of the textile industry. By embracing ZLD, the textile industry can not only mitigate its environmental impact but also ensure its sustainability and operational efficiency in an increasingly water-scarce world. As the industry continues to evolve, the adoption of advanced ZLD technologies will be crucial in securing a sustainable future for the textile sector.
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) is transforming wastewater management in the textile industry, offering a sustainable solution to water scarcity and pollution. While the implementation of ZLD involves significant costs and challenges, the long-term benefits in terms of water conservation, resource recovery, and regulatory compliance make it a viable and necessary investment. As the industry continues to evolve, the adoption of advanced ZLD technologies will be crucial in ensuring the sustainable growth of the textile sector.
Goldfinch Evaporation Systems is at the forefront of this revolution, providing comprehensive ZLD solutions that help textile industries achieve their sustainability goals. By embracing ZLD, the textile industry can not only mitigate its environmental impact but also secure its future in an increasingly water-scarce world.
Also Read: Increasing the Efficiency by 10x with the Steam Economy of Multiple Effect Evaporator Systems
Also get connected with us with LinkedIn..!!
Understanding Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD): Principles and Process
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) is a process used to treat industrial wastewater so that no liquid waste is released into the environment. Goldfinch Evaporation Systems is a leader in providing ZLD solutions, helping industries protect the environment and conserve water.
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) is a comprehensive approach to wastewater treatment that aims to eliminate any liquid waste from leaving the facility. This process is especially vital for industries that face stringent environmental regulations or operate in water-scarce regions. Goldfinch Evaporation Systems specializes in designing and implementing ZLD solutions that help industries reduce their environmental footprint, conserve water, and recover valuable resources.
What Is Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD)?
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) is an advanced wastewater management technique designed to completely remove liquid waste from an industrial facility. The primary goal of ZLD systems is to recover and recycle nearly all the water from wastewater streams, ensuring that only solid waste is left behind. This method is crucial for industries that need to comply with strict environmental standards or seek to minimize their water consumption.
Key Components of ZLD:
- Pre-Treatment: The first step involves filtering out large particles and adjusting the pH levels of the wastewater to prepare it for further treatment.
- Concentration: The wastewater is concentrated through evaporation or membrane processes to significantly reduce its volume.
- Crystallization: Remaining water is evaporated, leading to the formation of solid crystals from dissolved salts and other solids.
- Final Treatment: The solid waste is dried and either reused or disposed of safely.
How Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) Works:
Understanding the detailed workings of ZLD systems is essential to appreciate their complexity and effectiveness. Here’s a closer look at each stage of the ZLD process:
Pre-Treatment
Filtration: The initial stage of ZLD involves removing large particles and suspended solids from the wastewater using mechanical filters. This step is crucial to protect downstream equipment from damage and fouling.
Chemical Treatment: Chemicals are added to the wastewater to adjust its pH levels and coagulate dissolved solids. This preparation ensures that the wastewater is in an optimal condition for subsequent treatment stages.
Concentration
Evaporation: Thermal or mechanical evaporation methods are employed to remove a significant portion of the water content from the wastewater. This step greatly reduces the volume of liquid waste, concentrating the remaining water.
Membrane Processes: Technologies such as Reverse Osmosis (RO) and Nanofiltration (NF) further concentrate the wastewater by separating water from dissolved salts and organic compounds. These processes produce a high-quality permeate that can be reused within the facility.
Crystallization
Evaporative Crystallizers: These devices further evaporate the remaining water, resulting in the formation of solid crystals from dissolved salts and other solids. This stage is critical for achieving zero liquid discharge.
Salt Recovery: The solid by-products are collected and can sometimes be reused in other industrial processes or safely disposed of.
Final Treatment
Drying: Any remaining solid waste is dried to ensure that no residual moisture remains. This step is essential for converting the waste into a stable, non-leachable form.
Solid Disposal: The dried solids are either reused in other processes or disposed of in an environmentally safe manner, completing the ZLD process.
Benefits of Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD):
Implementing a ZLD system offers numerous benefits, which extend beyond mere regulatory compliance.
Environmental Protection
ZLD systems ensure that no liquid waste is discharged into the environment, thus preventing contamination of water bodies. This is particularly important in areas where industrial discharges could harm ecosystems and human health.
Water Conservation
By recovering and reusing water from wastewater streams, systems significantly reduce the demand for fresh water. This is crucial for industries operating in regions facing water scarcity.
Regulatory Compliance
Many industries face increasingly stringent regulations regarding wastewater discharge. ZLD systems help facilities meet these regulations by eliminating liquid effluent and reducing the environmental impact of their operations.
Resource Recovery
ZLD systems enable the recovery of valuable by-products, such as salts and minerals, from wastewater. These by-products can often be reused in other industrial processes, providing additional economic benefits.
Cost Savings
While the initial investment in ZLD systems can be substantial, the long-term savings from reduced water consumption, lower disposal costs, and potential revenue from recovered materials can make the investment worthwhile.
Applications of Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD):
ZLD systems are used across a wide range of industries, each with unique wastewater challenges. Here are some of the key applications:
Power Plants
Power plants generate large volumes of wastewater from processes such as cooling tower blowdowns. ZLD systems are used to treat this wastewater, recovering water for reuse and ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
Chemical and Petrochemical Industries
These industries produce complex wastewater containing hazardous chemicals. ZLD systems effectively treat this wastewater, recovering water and minimizing the risk of environmental contamination.
Textile and Dyeing Industries
Textile and dyeing operations generate wastewater with high concentrations of dyes and chemicals. ZLD systems are used to treat this wastewater, recovering water and reducing the environmental impact of these operations.
Mining and Metallurgy
Mining and metallurgical operations produce wastewater with high levels of heavy metals and other contaminants. ZLD systems are used to treat this wastewater, recovering water and ensuring safe disposal of solid waste.
Food and Beverage Industry
The food and beverage industry generates wastewater with high organic content. ZLD systems can treat this wastewater to recover water and reduce waste disposal costs, while also complying with strict hygiene and safety standards.
Challenges and Considerations in Implementing ZLD:
While ZLD systems offer significant benefits, they also come with challenges. Understanding these challenges is crucial for successful implementation.
High Costs
The initial investment and operational costs of ZLD systems can be substantial. This is due to the complexity of the technology and the energy-intensive nature of processes such as evaporation and crystallization. However, the long-term savings from reduced water consumption and lower waste disposal costs can offset these initial expenses.
Energy Consumption
ZLD systems require significant energy inputs, particularly for thermal evaporation processes. This can result in high operational costs and environmental impacts associated with energy use. Advances in energy-efficient technologies and the integration of renewable energy sources can help mitigate these concerns.
Complex Operation
ZLD systems involve multiple stages and require skilled personnel to operate and maintain. Ensuring that the system functions effectively and efficiently can be challenging, particularly for facilities with limited technical expertise. Comprehensive training and support from experienced providers like Goldfinch Evaporation Systems can help address these challenges.
Managing Solid Waste
While ZLD systems eliminate liquid discharge, they produce solid waste that must be managed. Ensuring the safe disposal or reuse of these solids is a critical consideration for any ZLD implementation. Proper planning and adherence to regulatory requirements are essential to avoid environmental and legal issues.
Goldfinch Evaporation Systems and ZLD:
Goldfinch Evaporation Systems is a leader in the design and implementation of ZLD systems. Our innovative solutions are tailored to meet the unique needs of each industry, ensuring optimal performance and sustainability.
Innovative Technologies
Goldfinch Evaporation Systems utilizes state-of-the-art technologies to achieve zero liquid discharge. Our systems incorporate advanced filtration, membrane processes, and evaporative crystallizers to ensure complete water recovery and waste minimization.
Customized Solutions
We understand that each industry and facility has unique wastewater treatment needs. Our team works closely with clients to develop customized ZLD solutions that meet their specific requirements and operational goals. This tailored approach ensures that our systems deliver maximum efficiency and effectiveness.
Commitment to Sustainability
At Goldfinch Evaporation Systems, we are committed to promoting sustainability and environmental protection. Our ZLD systems not only help industries comply with regulations but also contribute to water conservation and resource recovery. We strive to minimize the environmental impact of our solutions and support our clients in achieving their sustainability goals.
Expertise and Support
Our team of experts provides comprehensive support throughout the entire ZLD implementation process. From initial design and installation to ongoing maintenance and optimization, we ensure that our clients achieve the best possible outcomes. Our commitment to customer satisfaction and technical excellence sets us apart in the industry.
Case Studies: Success Stories with Goldfinch Evaporation Systems
Case Study 1: Power Plant
A major power plant faced challenges with cooling tower blowdown wastewater. By implementing a ZLD system designed by Goldfinch Evaporation Systems, the plant was able to recover 95% of the water, significantly reducing its freshwater consumption and ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
Case Study 2: Chemical Manufacturing
A chemical manufacturing facility was struggling with the disposal of hazardous wastewater. Goldfinch Evaporation Systems developed a customized ZLD solution that effectively treated the wastewater, recovered valuable chemicals for reuse, and eliminated liquid discharge.
Case Study 3: Textile Industry
A textile dyeing company implemented a ZLD system from Goldfinch Evaporation Systems to address its wastewater challenges. The system recovered 90% of the water, reduced the environmental impact of dye discharge, and enabled the reuse of water within the facility.
Future Trends in Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD)
The future of ZLD is shaped by ongoing technological advancements and increasing environmental awareness. Here are some key trends to watch:
Advanced Membrane Technologies
Innovations in membrane technologies, such as forward osmosis and advanced RO membranes, are enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of ZLD systems. These technologies offer improved water recovery rates and lower energy consumption, making ZLD more viable for a wider range of applications.
Integration with Renewable Energy
Integrating ZLD systems with renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, can reduce the environmental impact and operational costs associated with energy-intensive processes like evaporation. This approach aligns with the global shift towards sustainable and renewable energy solutions.
Digitalization and Automation
The adoption of digital technologies and automation is revolutionizing ZLD systems. Smart sensors, real-time monitoring, and automated controls enhance the performance and reliability of ZLD processes. These technologies enable proactive maintenance, optimize energy use, and improve overall system efficiency.
Focus on Resource Recovery
Future ZLD systems will increasingly focus on the recovery of valuable by-products from wastewater. Technologies for extracting and purifying salts, minerals, and other useful compounds will become more sophisticated, providing additional economic benefits and supporting the circular economy.
Conclusion:
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) is a critical solution for industries seeking to protect the environment, conserve water, and comply with stringent regulations. Goldfinch Evaporation Systems is at the forefront of delivering innovative, customized ZLD solutions that ensure water recovery, regulatory compliance, and economic benefits. As technology continues to advance, ZLD systems will become even more efficient and sustainable, offering greater opportunities for industries to minimize their environmental impact and promote resource conservation.
By partnering with Goldfinch Evaporation Systems, industries can achieve their ZLD goals and contribute to a more sustainable future. Our expertise, commitment to innovation, and focus on customer satisfaction make us the ideal choice for any organization looking to implement a ZLD system. Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you achieve zero liquid discharge and enhance your environmental stewardship.
Also Read: A Simplified Comparison : MEE vs. MVRE