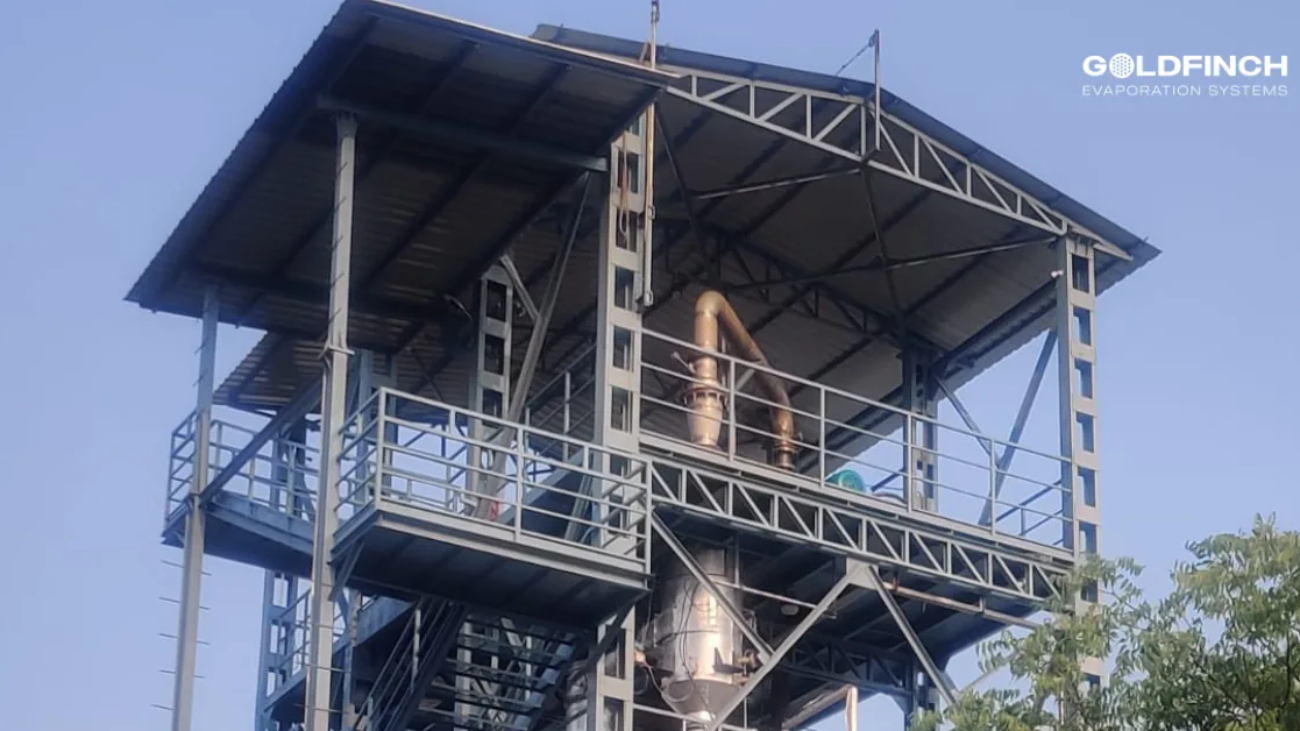
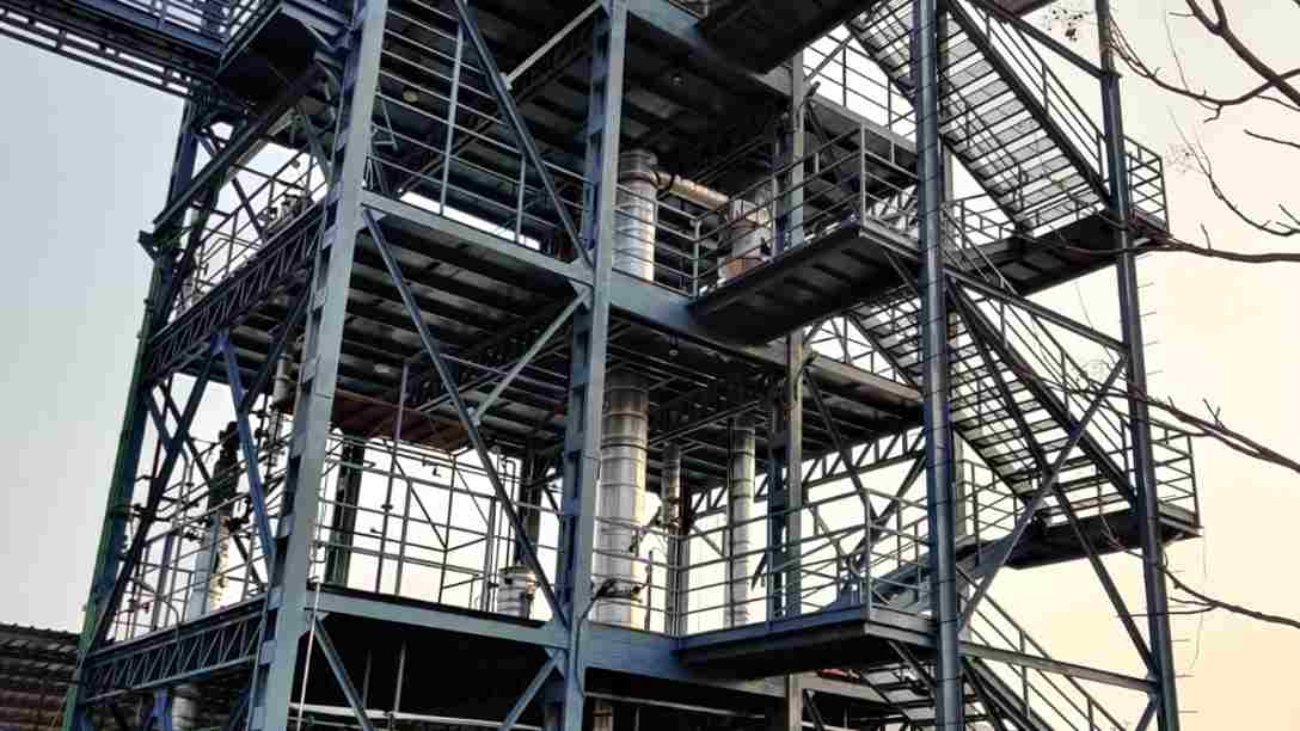
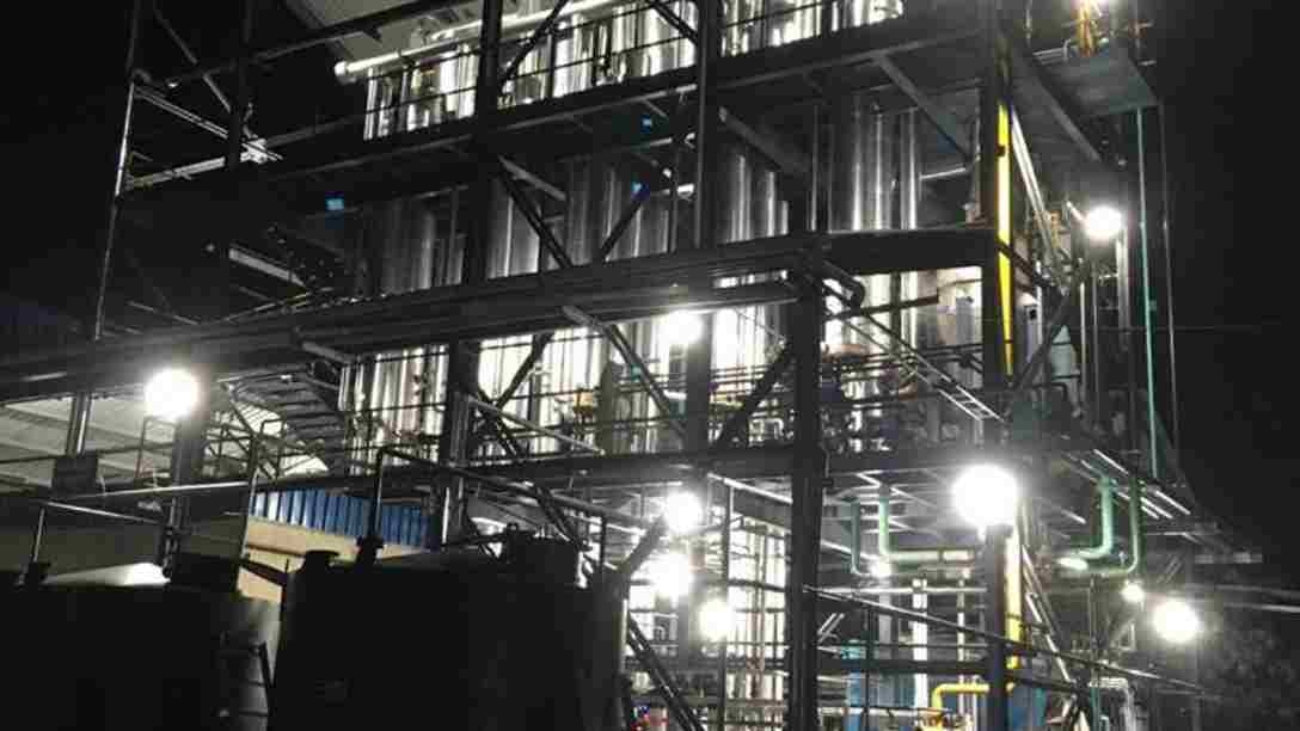
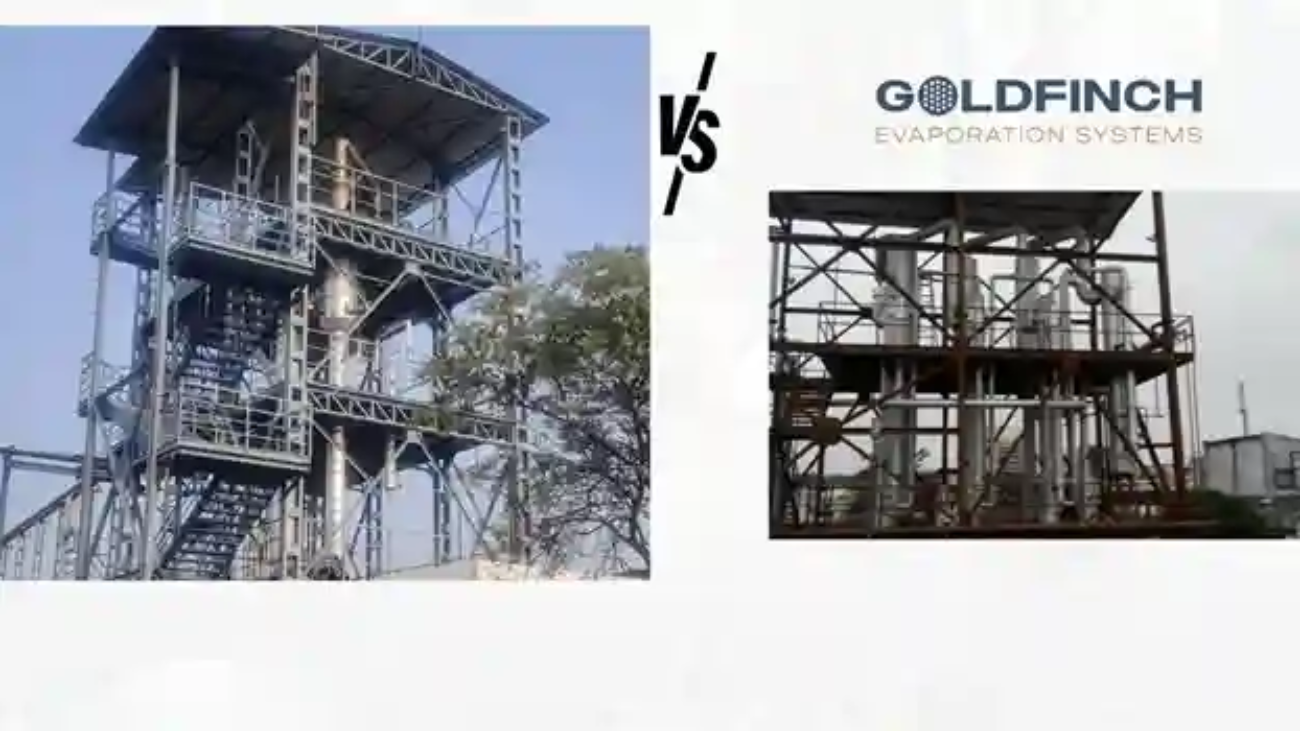
Industries today place huge importance on energy efficiency. Companies are looking at ways to reduce their operational costs and environmental impact. A mechanical vapor recompression system, or MVR evaporator, is the best way to achieve this.
Goldfinch evaporators, one of the leading manufacturers of evaporator systems, will help your business grow while being environmentally conscious. Let us see the working of MVR evaporators, with their uses and efficiency levels.
What is the principle of mechanical vapor recompression?
Mechanical vapor recompression is a method of recycling energy within the evaporation process. This is done by capturing the vapor generated during evaporation, compressing it using a mechanical compressor, and reusing it as the heat source for the next cycle.
The captured vapor, when compressed, rises in temperature and becomes pressurized. Thus providing the required heat for further evaporation and reducing the need for fresh steam. This principle of reusing vapor makes mechanical vapor recompression a sustainable choice for industries.
On the contrary, in a traditional evaporator, the steam once used is just released into the environment. Hence, an MVR evaporation method results in huge energy savings due to less requirement of hot vapor.
What is the use of MVR?
MVR evaporators are mainly used in industries requiring evaporation for concentrating liquids by the removal of water & other solvents. The recycling of water vapor makes this technology a cost-effective solution by reducing the use of steam boilers and other heating sources.
Major uses of MVR evaporator systems are:
- To reduce the overall operational energy costs
- To concentrate liquid waste for easier recycling or disposal
- To support sustainable initiatives
- To produce high-purity products for food processing and pharmaceuticals
Goldfinch evaporator has installed more than 50 evaporator systems for a varied set of clients. With a focus on quality and customer satisfaction, our customers are actively benefiting from the evaporators installed by us.
What are the applications of mechanical vapor recompression?
MVR evaporation technology has proven itself in many industries where evaporation is a vital step. Many industries also require custom-built MVR evaporators to best fit their usage and standards. The industries where mechanical vapor recompression systems are used are:
- Pharmaceuticals- The contents required for the manufacturing of pharmaceuticals go through MVR evaporators to ensure high-purity concentrates.
- Chemical Processing- MVR is used in concentrating the chemicals
- Wastewater treatment- To minimize wastewater generated during manufacturing and recover clean water for reuse
- Processing of food and drinks: Effective in reducing the water content in dairy products, juices, and other such items.
The process of mechanical vapor recompression proves beneficial for many of these industries.
What is the efficiency of MVR?
Mechanical vapor recompression systems are known for their efficiency. Compared to the traditional evaporator systems, which need a huge volume of fresh steam, MVR evaporators consume up to 90% less thermal energy.
Depending on the application, the specific energy consumption of MVR evaporators is as low as 25 kWh per ton of evaporated water. With such a drastic reduction in energy usage, industries benefit from lower operational costs and sustainable industrial processes.
Due to the clever design of the MVR evaporator, it doesn’t lose heat from previous cycles by continuously recycling and reusing the spent vapor. Goldfinch evaporators has pioneered this technology and successfully manufactures superior quality evaporation systems.
Goldfinch is the right choice for businesses needing customized evaporating and water treatment solutions.
What is the difference between MVR and TVR evaporators?
Both MVR (Mechanical Vapor Recompression) and TVR (Thermal Vapor Recompression) systems reuse vapor generated by them, but there are a few differences in how they operate.
- The MVR evaporator makes use of mechanical compressors or fans to compress and heat the vapor. A TVR evaporator uses a steam ejector for that purpose.
- An MVR evaporator only requires heat source in the beginning and then relies on electricity to run the compressors whereas a TVR evaporator needs additional heating for fresh steam generation.
- The initial investment for an MVR evaporator is on the higher side when compared directly with other traditional and TVR evaporator systems.
- An MVR evaporator ends up saving up to 90% less energy due to its reuse of steam. A TVR evaporator uses a higher energy for heating purposes.
- This means that in the long run, the running cost of the MVR evaporator is far less as compared to the TVR system.
Ultimately, a mechanical vapor recompression evaporator saves on energy bills, emits lower greenhouse gases, and also saves more in the long-term. A TVR system is less costly initially, but the higher running cost and low efficiency will build up over the years. TVR evaporators might be simpler but MVRE is the way towards the future.
To conduct a thorough analysis and know more about which evaporation solution can best fit your industry, contact Goldfinch Evaporators today.
How Does an MVR Evaporator Work?
Using the MVR evaporator plant requires a number of processes.
- Introduction of the Feed Solution: This is the liquid solution that will undergo evaporation.
- Compression and vapor generation: The mechanically produced vapor is compressed to increase its pressure and temperature.
- Heat exchange and evaporation: This compressed vapor’s thermal energy causes more liquid to evaporate.
- Collection of condensation: The extracted condensed vapor is either released or put back into the operation.
- Constant cycle: By repeating the procedure, energy conservation and continuous functioning are accomplished.
Conclusion: Why Choose Goldfinch MVR evaporator technology?
Goldfinch Evaporators boasts of being at the forefront of Mechanical Vapor Recompression Evaporation solutions with reliable, efficient, and eco-friendly systems across the globe. Using advanced MVR evaporator technology, We help companies optimize their operations without compromising sustainability and modernity. Our options are engineered to meet the specific needs of each industry to ensure better performance and minimal environmental impact.
If you’re looking to upgrade your operations with a sustainable and cost-effective evaporation system, Goldfinch Evaporators is here for you.
Check our LinkedIn page here.